
Alkane online lernen
This article is a summary of a YouTube video "Was sind Alkane und Isomere?!" by Chemie - simpleclub . TLDR Cows are a significant contributor to global warming due to their production of methane, and finding alternative sources of alkanes could help mitigate their impact on the environment.
Alkane einfach erklärt • Aufbau, Eigenschaften, Benennung · [mit Video]
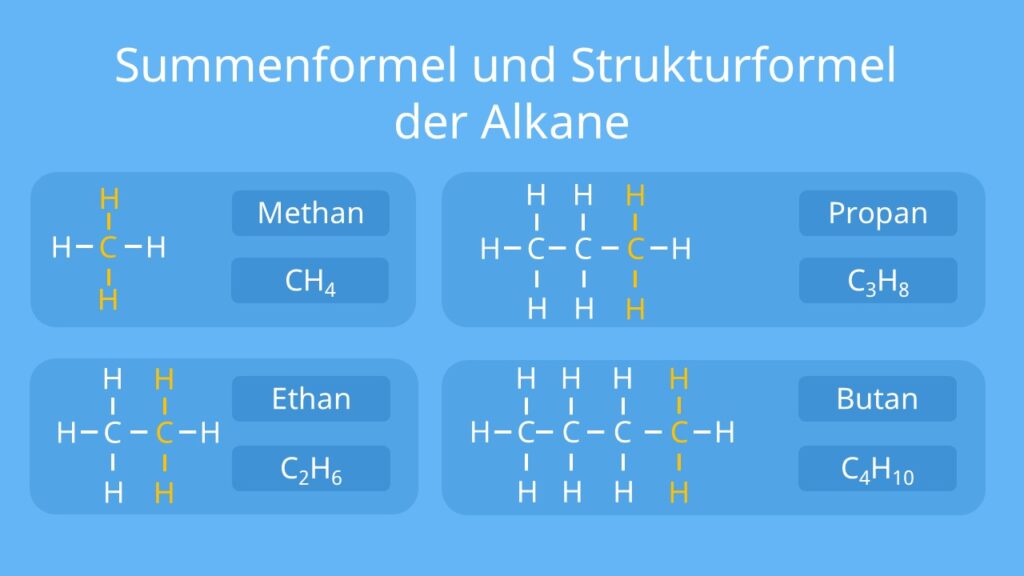
Alkanes are the simplest organic molecules, consisting solely of singly-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms. Alkanes are used as the basis for naming the majority of organic compounds (their nomenclature ). Alkanes have the general formula C n H 2n+2.

Nomenklatur der Alkane Cleverpedia
3.2 Alkanes and Alkane Isomers. Before beginning a systematic study of the different functional groups, let's look first at the simplest family of molecules to develop some general ideas that apply to all families. We saw in Section 1.7 that the carbon-carbon single bond in ethane results from σ (head-on) overlap of carbon sp3 hybrid orbitals.
Alkane Formula [with free study guide]
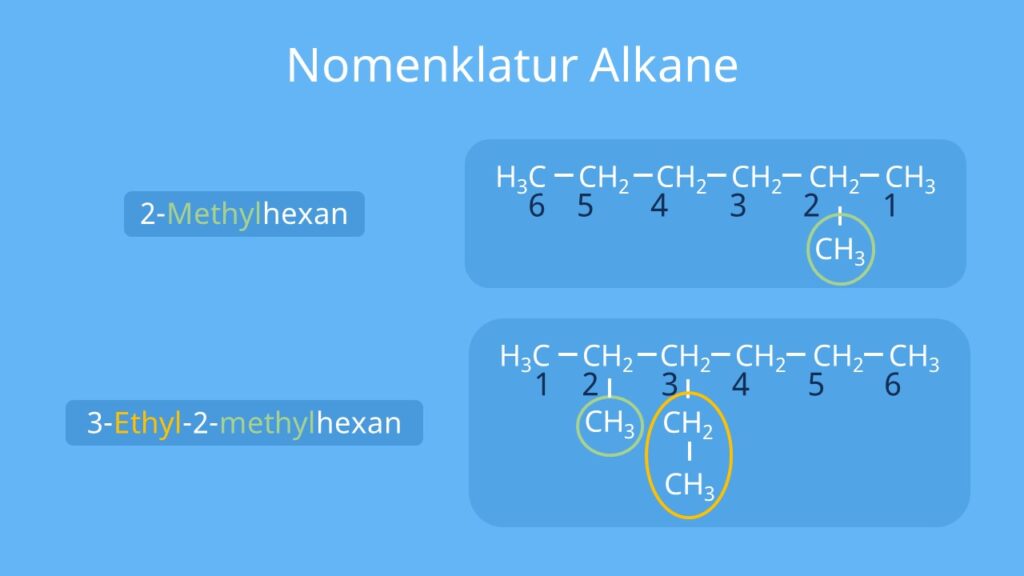
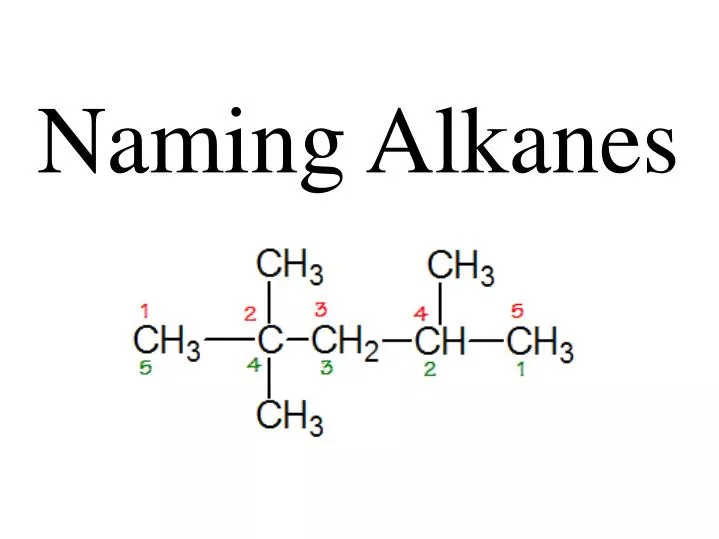
b) This alkane has a 6 carbon longest continuous chain length that we number from right to left to make the first methyl be C-2 (versus the opposite direction which would make the first methyl C-3). Since there are 3 methyl substituents at positions 2,3, & 4, this compound would have the name 2,3,4-trimethylhexane .
Alkane lernen mit Serlo!
Alkane. In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings ), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon-carbon bonds are single. [1] Alkanes have the general chemical formula CnH2n+2.

Naming Alkanes with Practice Problems Chemistry Steps
Alkanes. Alkanes, or saturated hydrocarbons, contain only single covalent bonds between carbon atoms.Each of the carbon atoms in an alkane has sp 3 hybrid orbitals and is bonded to four other atoms, each of which is either carbon or hydrogen. The Lewis structures and models of methane, ethane, and pentane are illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\).

Lernpfad zur IUPACNomenklatur der Alkane Medienbildung
Genauer gesagt sind sie ungesättigte Kohlenwasserstoffe, da sie mindestens eine Doppelbindung besitzen. Alkine sind ebenfalls ungesättigt, allerdings besitzen sie mindestens eine Dreifachbindung. Alkane hingegen sind gesättigt, das heißt, sie sind lediglich über Einfachbindungen verknüpft.
Alkane einfach erklärt • Aufbau, Eigenschaften, Benennung · [mit Video]
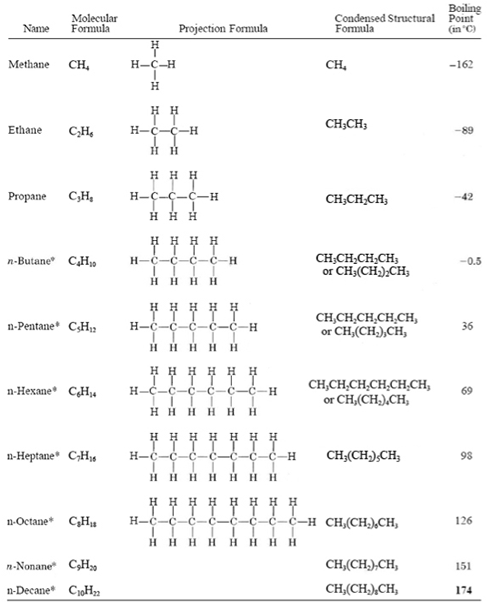
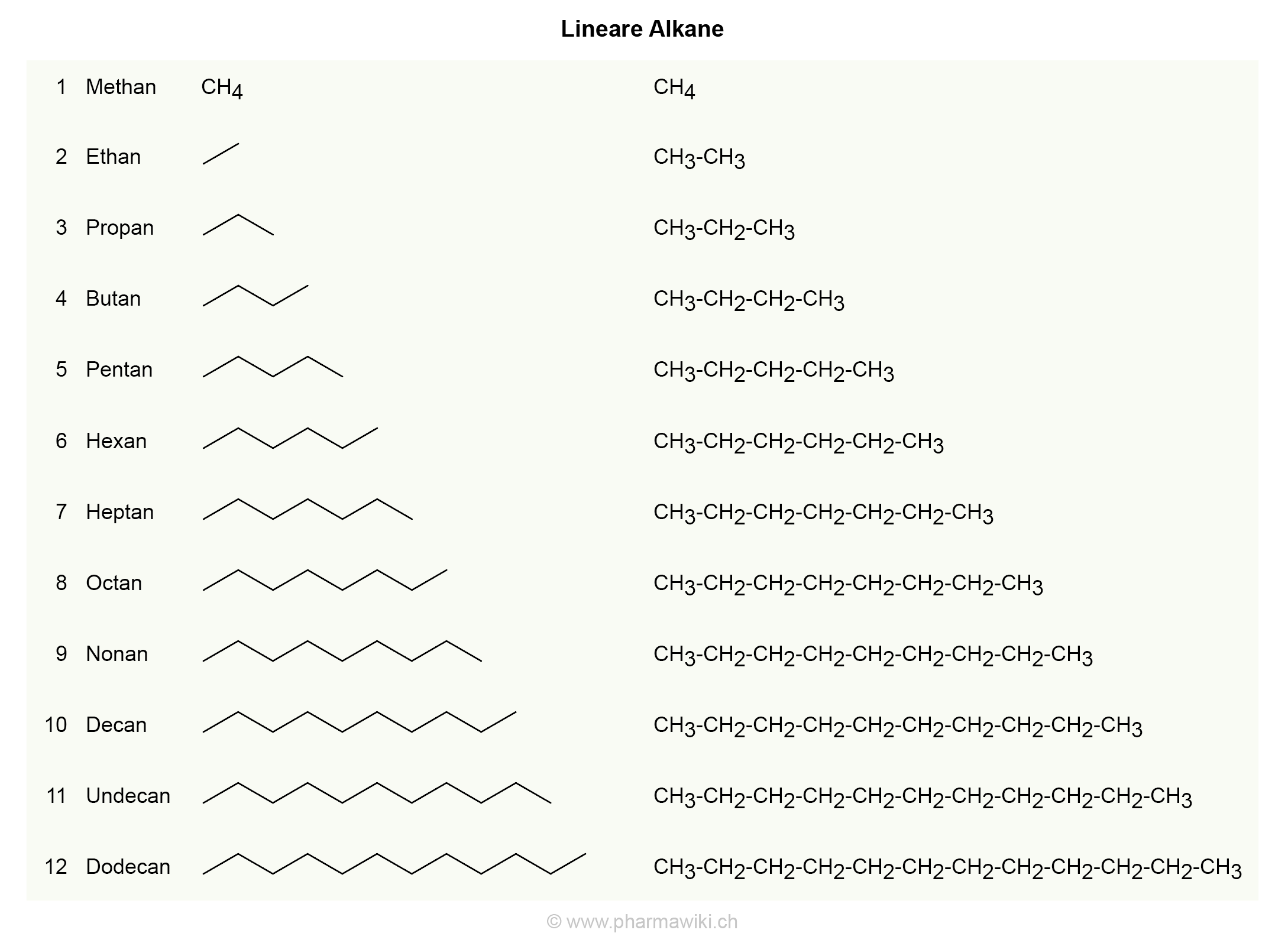
Alkanes. The alkanes are a subset of hydrocarbons whose names all end in -ane. The names, molecular formulae and the structural formulae of the first eight alkanes must be learned. Using a.
PPT Naming Alkanes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4845709
Als Alkane ( Grenzkohlenwasserstoffe, früher Paraffine) bezeichnet man in der organischen Chemie die Stoffgruppe der gesättigten, acyclischen Kohlenwasserstoffe. Das heißt, ihre Vertreter bestehen nur aus den beiden Elementen Kohlenstoff (C) und Wasserstoff (H), weisen nur Einfachbindungen und keine Kohlenstoffringe auf.
PharmaWiki Alkane
Alkane (früher: Paraffine) sind eine Stoffgruppe in der organischen Chemie. Dabei handelt es sich um gesättigte Kohlenwasserstoffe, die nur Einfachbildungen enthalten. Ihr Aufbau kann grob in unverzweigt und verzweigt unterteilt werden.

Alkane Structures YouTube
Alkanes are simplest organic compounds that consist of single bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms with the general formula CnH2n+2 . Alkanes are solid, liquid or gas at room temperature depending on the size of their molecules.To learn detailed structures, formulas, and Physical Properties of Alkanes with FAQS and Videos, Visit BYJU'S for more information.

Alkanes (ALevel) ChemistryStudent
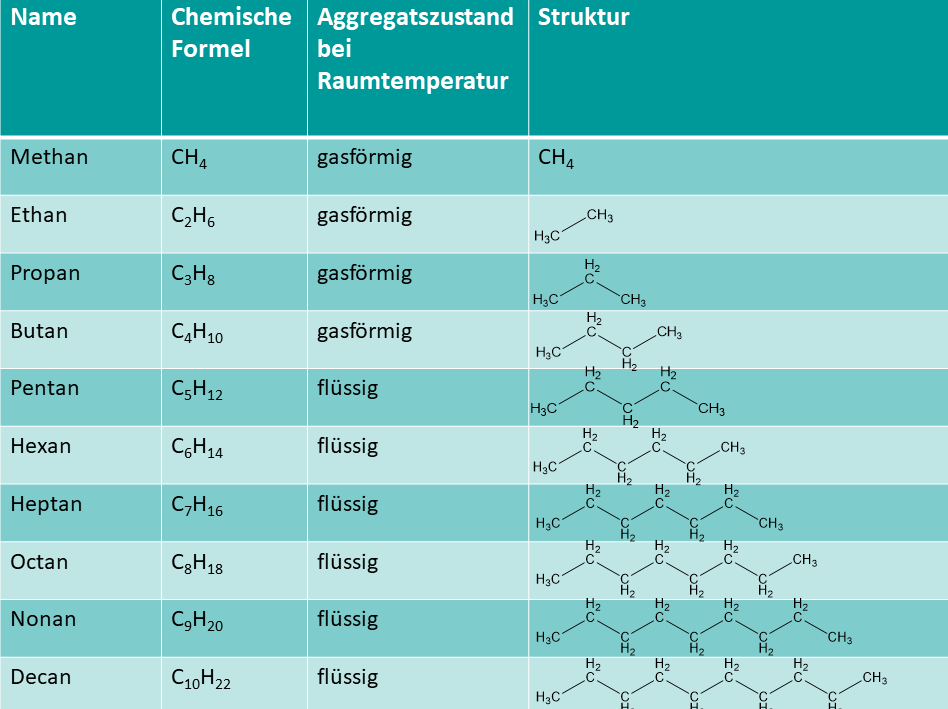
Ist ein Stoff gasförmig besitzen dessen Teilchen einen großen Abstand zueinander. Ist ein Stoff fest besitzen dessen Teilchen einen ziemlich kleinen Abstand zueinander. Die unterschiedlichen Aggregatzustände werden durch verschiedene Schmelz- und Siedepunkte bewirkt: Verzweigte Isomere

Homologe Reihe der Alkane
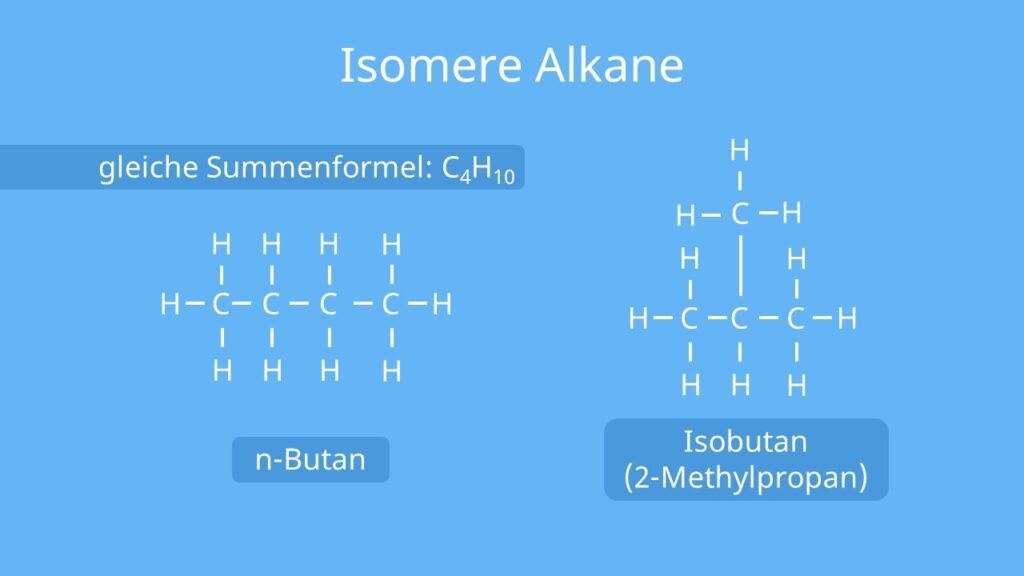
Exercise 3.2.7 3.2. 7. Draw the 5 constitutional isomers of C 7 H 16 (of the 9 total isomers possible) that have 5 carbons as the longest carbon chain length. Answer. Alkanes are organic compounds that consist entirely of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms and lack any other functional groups. Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2 and.
Alkane einfach erklärt • Aufbau, Eigenschaften, Benennung · [mit Video]
Using Common Names with Branched Alkanes. Certain branched alkanes have common names that are still widely used today. These common names make use of prefixes, such as iso-, sec-, tert-, and neo-.The prefix iso-, which stands for isomer, is commonly given to 2-methyl alkanes.In other words, if there is methyl group located on the second carbon of a carbon chain, we can use the prefix iso-.

Nomenklatur von Alkanen (IUPAC Halogenalkane Organische Chemie) 5 YouTube
Molecular Formulas. Alkanes are the simplest family of hydrocarbons - compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only. Alkanes only contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and carbon-carbon single bonds. The formula of any of the alkanes follow the general formula CnH2n+2 C n H 2 n + 2 . The first six alkanes are tabulated below:

Alkane einfach erklärt • Aufbau, Eigenschaften, Benennung · [mit Video]
An alkane is not a functional group. An alkane is a hydrocarbon compound with the general formula CnH2n+2. An alkyl group is an alkane that has a hydrogen atom missing. There is an unfulfilled single bond coming off the C atom that has lost the H atom. Thus, CH3CH3 is ethane (an alkane), but CH3CH2— is an ethyl (alkyl) group.